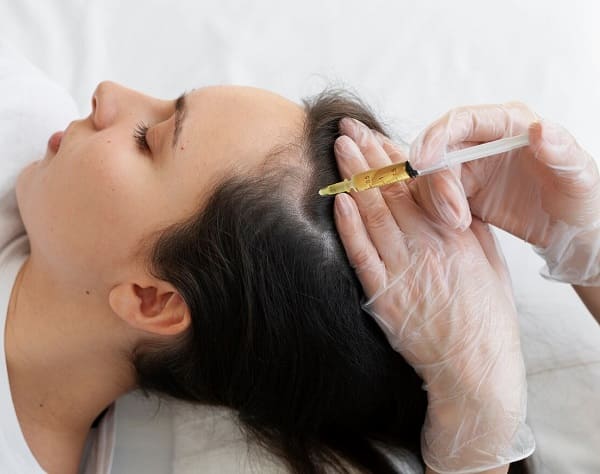
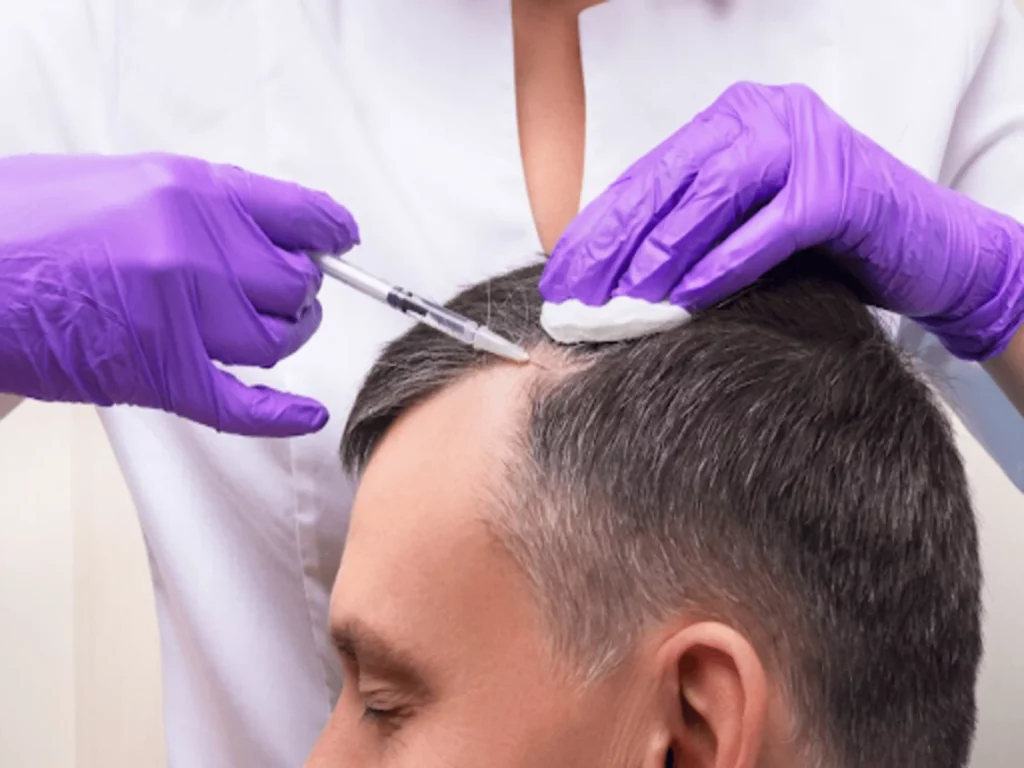
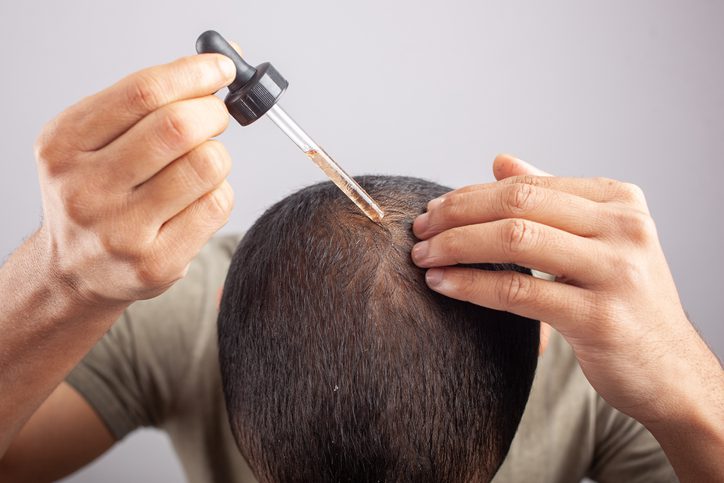
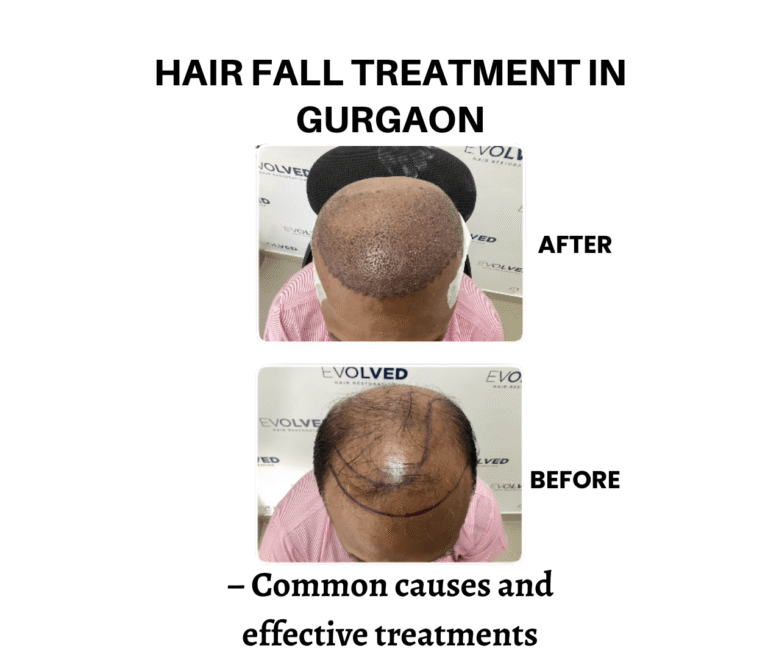
Hair loss or baldness is often perceived as predominantly a male concern. But did you know millions of women around the globe silently struggle with bald patches, hair thinning, and receding hairlines? Can women get hair transplants?
If you’re a woman experiencing any of this, please know you are not alone. And the world has options for you- Safe Hair Transplant Procedures. This procedure, which was once centered around the male population, has successfully entered women of society as well to address hair loss and hair thinning in women.
This comprehensive guide is curated specifically for you to walk through the world of hair transplantation. Whether you’re just beginning to explore your options or ready to take next step, bookmark this guide as your hair transplant bible for making informed decisions.
Hair Loss: A Common Issue for Women Globally
Hair has long been associated with femininity, women’s expression of self, and most importantly, beauty. For most women, hair is not just a part of their appearance; they are their IDENTITY. So when hair starts falling out, thinning, or bald patches become visible, they affect women deeply and psychologically.
According to the National Council on Aging, “As many as 40% of people with hair loss are women.” This is a critical statistic, depicting how hair loss is not just a man’s concern but is affecting millions of women worldwide.
Female Hair Loss: Understanding the Causes and Patterns
Hair loss in females is complex, and it is significantly different from patterns of baldness seen in males. It is crucial to understand the underlying causes so as to determine if hair transplant is the right solution.
Hair loss in women is a distressing issue. It is often stemmed with multiple internal and external factors. Female hair loss is usually more diffuse and less recognizable, unlike the baldness pattern seen in males, making the entire course of diagnosis and treatment more nuanced.
1. Androgenetic Alopecia (Female Pattern Hair Loss)
This is the most common form of hair loss in women, about 40% of women who stand for hair loss.
- Cause: A hereditary sensitivity to male hormones such as androgen (DHT) leads to gradual shrinkage of the hair follicles.
- Pattern: Usually manifests as a wide range, spreading thinness on the crown, and an intact frontal hairline.
- Progress: This is an old, progressive situation, but it can be controlled or slowed with initial intervention.
2. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal ups and downs can affect the growth cycle of hair. Common hormonal triggers include:
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS): Elevated change can reduce the hair on the skull and increase the hair on the face/body.
- Pregnancy and postpartum Changes: A bounce in estrogen during pregnancy promotes hair growth, but a strong drop of postpartum leads to telogone effluvium (temporary shed).
- Menopause: A reduction in estrogen and progesterone levels results in thin hair and increases the sensitivity of androgens.
- Thyroid disorder: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can interfere with the hair growth cycle.
3. Autoimmune Disorders and Other Medical Conditions
Many health conditions directly affect the hair follicles:
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition where the immune system happens to attacks the hair in the hair and causes baldness.
- Lupus: Arrling can cause alopecia if not treated.
- Anemia (iron deficiency): Follicles reduce oxygen supply, causing weak, crispy hair.
Chronic disease or surgery can shock the hair cycle and cause excessive shedding after the phenomenon (telogenic effects).
4. Prolonger medical treatments and medications
Some medical treatments can partially disrupt the natural hair growth cycle by pushing follicles into resting stage. Some of these treatments include:
- Chemotherapy drugs (cytotoxic agents)
- Beta-blockers (used for blood pressure)
- Antidepressants
- Oral contraceptives (especially those high in androgens)
- Steroids (prolonged use)
- Retinoids (like isotretinoin for acne)
Hair loss as a side-effect of medication usually reverses after discontinuation, but this may take several months for hair to grow back.
5. Deficiency of Nutrition
The scalp and follicles require proper nutrients for the growth of healthy hair. Deficiencies can lead to a significant hair shed.
- Iron: Red blood is important for cell production and oxygen supply.
- Zinc: The follicle supports health and DNA synthesis.
- Vitamin D: Important to stimulate inactive hair follicles.
- Biotin (vitamin B7): Keratin supports production.
- Protein: Hair is mainly made of keratin, a protein. Low protein intake causes slow hair growth.
Crashing dieting, restrictive eating habits or underlying digestive problems (such as celiac disease) may occur.
6. Stress, Physical or Emotional
Stress not only affects the mind; It can deeply disrupt the positive cycle.
- Telogen ephluvium: A physical or emotional shock can lead to a large number of hairs pushing into the resting phase.
- Triggers: High fever, surgery, birth, grief, or psychological trauma.
- Timeline: shedding usually occurs 2-3 months after a stressful event and can last for months.
However, temporary, chronic stress can eliminate and delay the cycle of hair loss.
7. Traction Alopecia
It is a form of hair loss due to frequent hair stress, often caused by some hairstyles.
- Causes: Close ponytail, braids, buns, hair extensions, or inappropriate wig usage.
- Impact: Permanent scarring can occur if it is not addressed quickly and if not addressed early.
It is usually seen in women and can be completely reversible if they are caught early.
8. Regular Styling or Environmental Factors
Daily styling habits can help thin hair over time:
- Excessive heat style (blow dryer, dishes)
- Chemical remedies (bleaching, rest, permission)
- Exposure to hard water: Hard water minerals can be deposited on the skull.
- Pollution: Particle-shaped material can damage and weaken toxin scalp and weaken hair.
Reducing exposure and using headgear can help reduce damage.
Summary Table: Causes of Hair Loss in Women
| Cause | Description | Reversibility |
| Androgenetic Alopecia | Genetic, hormone-sensitive hair thinning | Manageable but not reversible |
| Hormonal Imbalances | PCOS, thyroid issues, and menopause | Reversible with treatment |
| Medical Conditions | Autoimmune disorders, anemia | Depends on condition |
| Medications | Side effects from drugs | Often reversible |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | Iron, vitamin D, and protein | Reversible with supplementation |
| Stress (Telogen Effluvium) | Physical/emotional trauma | Usually reversible |
| Traction Alopecia | Repetitive pulling hairstyles | Reversible if caught early |
| Environmental/Styling Damage | Heat, chemicals, pollution | Manageable with care |
Female Hair Loss Patterns: Understanding How Women Lose Hair Differently
While hair loss in women is less obvious, it is still equally emotionally distressing. Most men face a pattern of hair loss with receding hairlines and bald patches, but women usually experience a more subtle and diffused thinning. Therefore, recognizing these patterns in women is essential for early detection and treatment.
Let’s understand it better:
Progress of Hair Loss in Females
The most common type of hair loss in women is androgenic alopecia, often called female pattern hair loss (FPHL). It usually begins with a gradual reduction in hair density instead of suddenly developing bald patches.
- The hair looks thin, and the amount decreases
- The skull appears more, especially under bright light
- The hair part begins to expand, especially in the center of the skull
- Unlike male pattern baldness, the frontal hairline remains intact
- More hair in brushes, pillows, and drains – especially after washing or styling
Ludwig Classification: A Standard Way to Understand Female Hair Loss Patterns
Doctors commonly use the Ludwig Scale to categorize the severity of female pattern hair loss. It has three main stages:
▶ Type I – Mild
- Slight thinning on the crown or top of the head
- The parting line begins to widen slightly
- Hair loss may be barely noticeable to others
- Often mistaken for seasonal shedding or stress-related hair fall
▶ Type II – Moderate
- Noticeable thinning across the mid-scalp
- Wider central parting with reduced volume on the sides
- Hair doesn’t respond well to styling; more scalp is visible
- This is often the stage when women begin seeking medical advice
▶ Type III – Severe
- Extensive thinning at the crown with visible scalp
- Hair is very thin or absent across the top of the head
- The hairline is still usually preserved, but density is drastically reduced
- This stage may require surgical intervention like a hair transplant
Note: The Ludwig Scale is different from the Norwood Scale, which is used to assess male pattern baldness. This distinction is important because treatments and transplant strategies differ significantly between genders.
Diffuse Thinning vs Patterned Loss
Women can also experience diffuse thinning, which means the hair becomes thin across the entire scalp, without a specific pattern. This is common in conditions like:
- Telogen Effluvium (temporary shedding from stress, illness, or medications)
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Chronic illnesses
In such cases, the entire scalp appears thin, but no particular zone is balder than another, making it harder to pinpoint the cause without medical evaluation.
Specific Areas Affected in Female Hair Loss
| Scalp Region | Common Observations |
| Crown/Vertex | Most visible thinning; parting line expands here |
| Mid-scalp | General loss of volume; hard to style, lacks bounce |
| Hairline | Usually remains intact, but may slightly thin with age |
| Temporal region (sides) | Less commonly affected; may thin if stress-related |
Why Understanding Patterns Matters
Identifying your hair loss pattern can help:
- Diagnose the underlying cause (hormonal, nutritional, genetic, etc.)
- Choose the right treatment, whether medical or surgical
- Set realistic expectations about what results you can achieve
For instance:
- Women with stable thinning at the crown may benefit from FUE or Direct hair transplant.
- Women with diffuse unpatterned thinning may be better suited for non-surgical treatments like PRP, minoxidil, or laser therapy.
Hair loss in women is not just a cosmetic problem – it is a deep, individual issue. Understanding how female hair loss presents itself, you get a clear way to find the right solution, whether it is medical treatment, lifestyle changes, or consult with hair transplant surgeon.
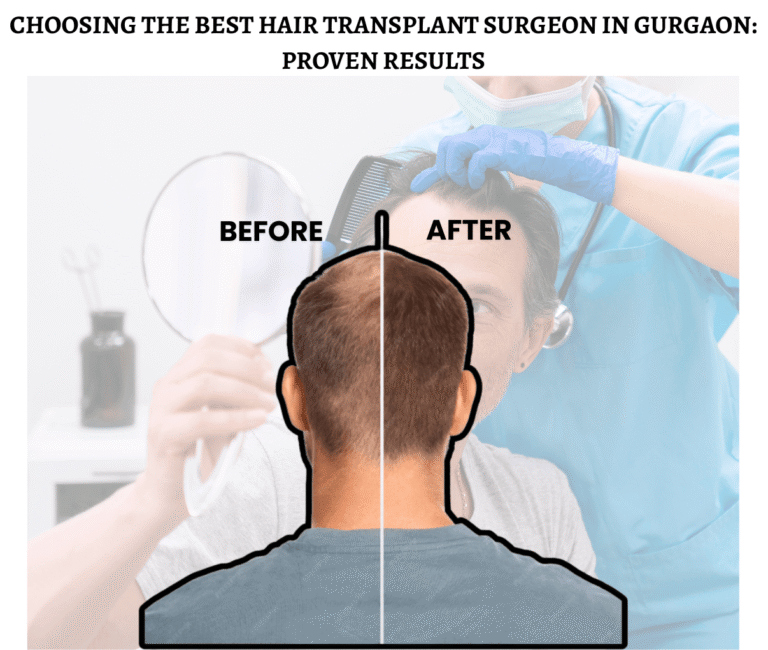
If you are unsure of the cause of your pattern or hair loss, our experienced experts at at the Gurgaon branch of Evolved Hair India can provide a comprehensive diagnosis and customized care plan – so you can regain both your hair and your self-confidence.
Can Women Get Hair Transplants Surgery?
Not every woman experiencing hair loss is a candidate for hair transplant surgery. The ideal candidates typically include:
Suitable Candidates:
- Women with mechanical or traction alopecia (e.g., from tight hairstyles)
- Women with stable hair loss patterns
- Women who have undergone plastic surgery and wish to restore hair in the scarred areas
- Women with localized bald spots, rather than diffuse thinning
Unsuitable Candidates:
- Women with diffuse unpatterned alopecia (DUPA), where donor hair is also thin
- Those with active autoimmune diseases causing hair loss
- Women experiencing temporary hair shedding, such as telogen effluvium
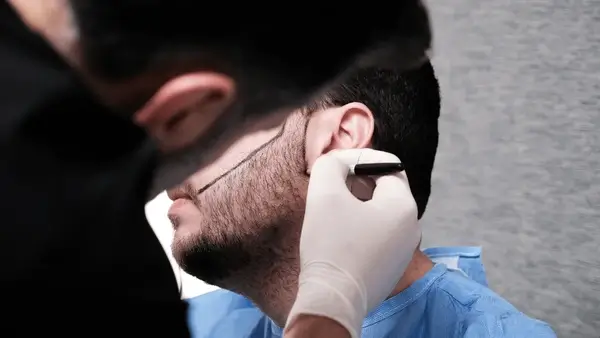
A proper dermatological and trichological evaluation is essential before considering surgery. At our clinic in Gurgaon, we conduct in-depth scalp analysis, hormone profiling, and follicular density mapping before recommending any surgical intervention.
Read More: Hair Transplant and Mental Health: A Closer Look at the Connection
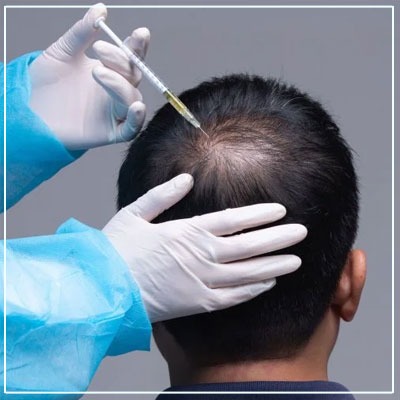
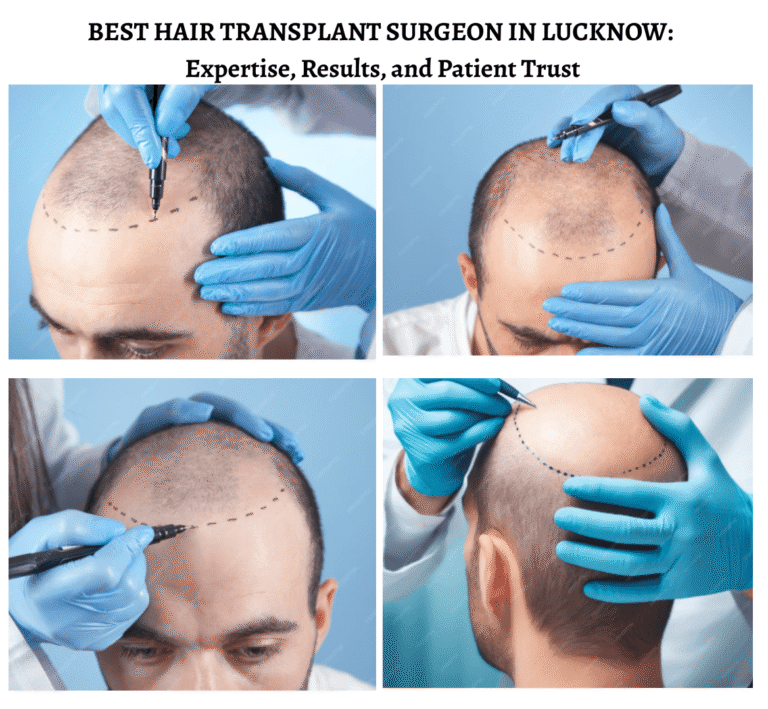
Types of Hair Transplants Suitable for Women
Hair transplant procedures have evolved, and several methods are now available that are effective and minimally invasive.
1. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
- A strip of scalp is removed from the donor area (usually the back of the head).
- Hair follicles are extracted and implanted in the recipient area.
- Leaves a linear scar, which can be concealed with longer hair.
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- Individual hair follicles are extracted and implanted.
- Minimal scarring and faster healing.
- Preferred for women who want to avoid a linear scar.
3. Direct Hair Implantation
- A variation of FUE that uses a pen-like tool for precise implantation.
- Offers greater control over angle, direction, and density.
Each technique has its own pros and cons. FUE and Direct Hair Implantation are often favored for women due to their minimally invasive nature and minimal downtime.
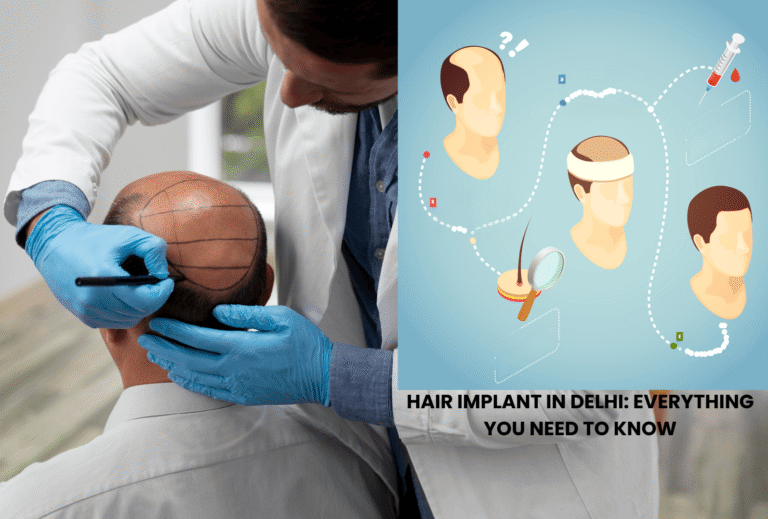
What to Expect Before, During, and After the Procedure
Pre-Surgery Preparation
- Consultation & Diagnosis: A scalp evaluation, health history review, and sometimes blood tests or hormonal assessments are conducted.
- Medication Review: You may be asked to stop certain medications prior to surgery.
- Scalp Preparation: Includes cleansing, trimming, and marking recipient areas.
During the Procedure
- Usually performed under local anesthesia
- Can take 4–8 hours, depending on the number of grafts
- You remain awake and comfortable throughout
Post-Surgery Recovery
- Mild swelling and tenderness in the first 3–5 days
- Tiny scabs may form and fall off in 7–10 days
- Transplanted hair may shed after a few weeks—this is normal
- New growth begins in 3–4 months, with full results in 9–12 months
Risks, Limitations & Expected Results
Risks:
- Temporary swelling, redness, or discomfort
- Folliculitis (infection of follicles), which is rare and treatable
- Uneven growth if not done by an experienced surgeon
- Overharvesting from the donor site can lead to thinning
Limitations:
- Women with widespread thinning may not have sufficient donor hair
- Results depend on the quality of the donor area and overall health
- Success varies with adherence to aftercare and overall lifestyle
Expected Results:
- Natural-looking hairline and improved volume
- Increased confidence and self-esteem
- Results are permanent but may require maintenance
Alternatives to Hair Transplants for Women
Before proceeding with surgery, it’s crucial to explore non-invasive treatments, especially in early or mild cases of hair loss.
Non-Surgical Options Include:
- Minoxidil (5% topical): FDA-approved treatment for female pattern hair loss
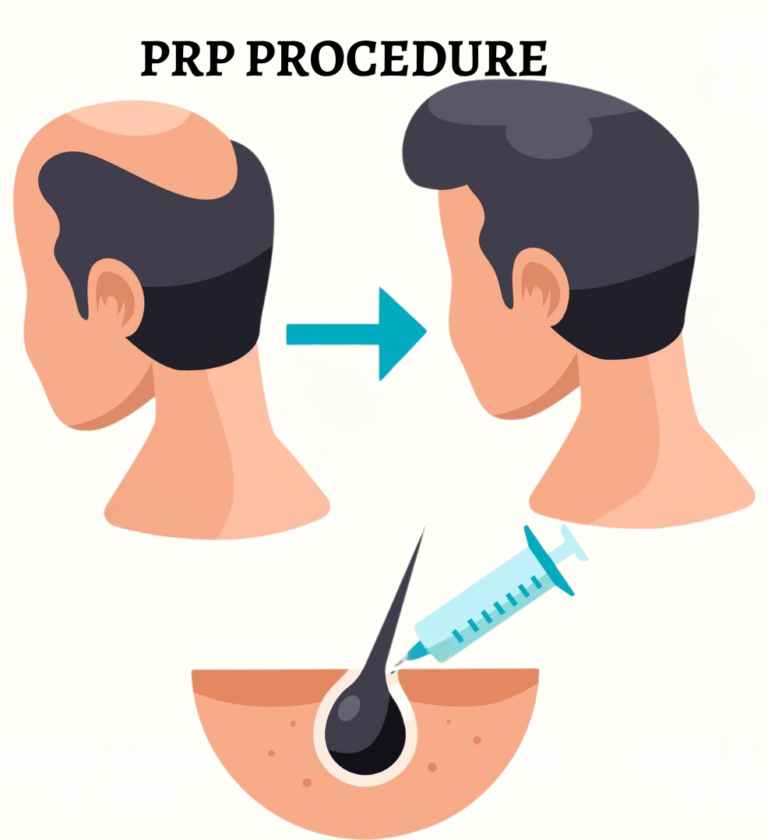
- PRP Therapy: Uses your own platelets to stimulate dormant follicles
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Encourages hair regrowth using light energy
- Microneedling + Serums: Enhances blood flow and nutrient delivery
- Nutritional Supplements: Biotin, zinc, iron, and vitamin D
These therapies can be used alone or alongside a transplant for optimal results.
Read More: Hardik Pandya Hair Transplant: Unveiling the Truth
What Makes Evolved Hair India the Best Hair Transplant Clinic in Gurgaon
Choosing the right clinic plays an important role in the success of your hair transplant. At Evolved Hair India, we specialize in women’s hair transplant processes with a patient-first, holistic approach.
What distinguishes us:
- Dermatologist and trichologist with 10+ years of experience
- Advanced techniques such as FUE for women
- State-of-the-art facilities ensure sterile, safe procedures
- Personalized Eastern and Postoperative Parliament Plan
- Depth hormonal and lifestyle assessment
- Wise, auxiliary environment designed for female patients
Women from all over Gurgaon and NCR trust us not only for results, but also for compassionate care and professionalism that control each consultation.
If you are looking for the best hair transplant clinic in Gurgaon, our team at Evolved Hair India invites you to a personal consultation to find your options confidently and safely.
In the End: Empower Your Confidence with the Right Solutions
Hair loss can be an emotionally disturbing experience for women, who often experience self-confidence, relationships, and self-image. But today, science and surgical progress have made a realistic and effective alternative for women.
Whether you are scared of genetic hair thinness, postpartum, or previous processes, the first step is to understand your situation and search for the right solution. A well-done hair transplant can not only restore your hair but also your feelings.
Ready to take the next step? Book your confidential consultation with our experts at Evolved Hair India and find out if a female hair transplant in Gurgaon is the right way for you.